A Practical vmc Guide at a Glance
Notes extracted from Cloud Foundry Support.
For more information: vmc -h, or vmc help.
General Account
Identify yourself to Cloud Foundry’s cloud with your account information:
- vmc login youremail@email.com –passwd yourpassword
- vmc login –email youremail@email.com –passwd yourpassword
vmc passwd
Change your password.
vmc logout
Updating vmc
vmc is provided as a Ruby gem is often updated with new commands and options, so be sure you have the latest version, at the command line:
gem update vmc
Non-Interactive/Suppressing Prompts
By default vmc operates in an interactive mode and many operations will follow-up with multiple prompts asking for options. To use vmc in interactive mode and provide options in the command itself:
vmc command -n –options
Example: vmc push app -n will push the application to the cloud and take all defaults without prompting.
vmc help options
Displays commands and all options which can be used as parameters on the command line
Configuration
vmc target
Displays URL for cloud targeted by vmc client.
vmc target url
Successfully targeted to [http://api.cloudfoundry.com]
vmc info
Confirms target cloud, vmc client, user and usage.
vmc apps
Lists applications for your account, number of instances, running/stopped, URLs, and associated services.
Deploying and Application
vmc push
Executed in the directory containing your application; asks for application name, URL, application type, memory allocation, and whether any services will be bound to it. Pushes an application up to the cloud, stages and starts it.
vmc push appname
Updating Applications
vmc update
Note: This may cause an existing application to drop user requests if the application is available to others.
To update an application without downtime, we add the application as a new one associated with the existing URL, disassociate the old version from the URL, then delete the old one:
vmc push appNEW
(At this point bind any shared services, like DB, Cache, etc.)
Test appNEW.cloufoundry.com
vmc map appNEW app.cloudfoundry.com
Associate new application with existing URL.
Test app.cloudfoundry.com, including existing functionality
vmc unmap appOLD app.cloudfoundry.com
Does not drop traffic; stops all new traffic to old application
Test app.cloudfoundry.com
vmc delete appOLD
Monitoring and Management
vmc info
Displays information about your cloud foundry account, client, and total resources consumed
vmc list
Displays your applications on the cloud and their status (running/stopped/resources)
vmc logs appname
Displays standard output logs for the application
vmc crashlogs appname
Displays any fatal errors that occurred for an application. If none, displays standard output.
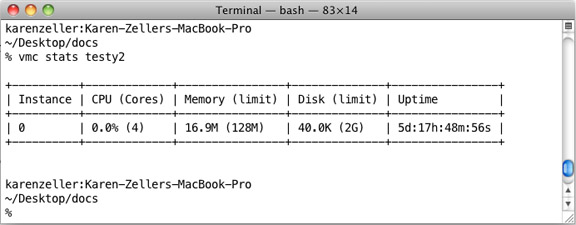
vmc stats appname
Displays resource consumption for application
vmc instances n
Adds or removes instances of an application in your cloud
Cloud Foundry Services
vmc services
Lists services available and provisioned for your cloud
vmc create-service servicename
Creates an instance of the service
vmc bind-service servicename appname
Binds a service to a cloud application
vmc unbind-service servicename appname
Unbinds service from named application
vmc delete-service servicename
Removes a provisioned service from your cloud
vmc push
Select Yes for prompt “Would you like to bind any service to ‘appname’”
Specify whether you want to bind to an existing service
Select the number of the existing provisioned service you will bind
vmc update
Stop your running application before you update: vmc stop appname
vmc update
vmc start appname